Recently, a team from Pune based ICMR-National Institute of Virology noted India as an endemic reservoir for the Chikungunya virus with persistent global transmissions from the country. The dispersal of the strains from India was noted to neighbouring and distant countries such as Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and China.
Daily Current Affairs Quiz 2020
Key-Points
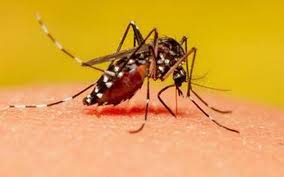
Chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted to humans by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes.
It is caused by an RNA virus that belongs to the alphavirus genus of the family Togaviridae
It causes fever and severe joint pain and other symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue and rash.
The disease shares some clinical signs with dengue and zika and can be misdiagnosed in areas where they are common.
The disease mostly occurs in Africa, Asia and the Indian subcontinent. However, a major outbreak in 2015 affected several countries of the Region of the Americas.
There is no specific antiviral drug treatment for chikungunya and treatment is directed primarily at relieving the symptoms, including the joint pain using antipyretics, optimal analgesics and fluids.
Prevention and control relies heavily on reducing the number of natural and artificial water-filled container habitats that support the breeding of the mosquitoes. This requires mobilization of affected communities.





