Scientists detect ionospheric irregularities during major space weather events that influence communication & navigation systems. The scientists also found that enhanced winds during geomagnetic storms can either add or suppress the existing ion densities to produce either positive or negative stormsthat modify the electrodynamics of the ionosphere, thereby influencing navigation and communication that form a crucial part of our lives.
Daily Current Affairs Quiz 2020
Key-Points
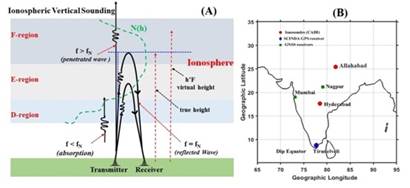
The Earth’s magnetic field lines are nearly horizontal over magnetic equator due to which equatorial ionosphere is a bed for a variety of plasma instabilities to cause plasma disturbances and plasma irregularities.
These plasma irregularities pose severe problems to the communication and navigation systems and interfere with surveillance operations as well as disruption in detection and tracking of aircraft, missiles, and satellites.
Understanding the thermosphere‐ionosphere-magnetosphere interactions that control the electrodynamics behind dynamical evolution of ionospheric irregularities under disturbed periods like geomagnetic storms is most important in developing and maintaining communication and navigation systems.
The electrodynamics under these major space weather events was studied using the chain of a ground-based special type of radar Doppler ionosondes along with GPS Receivers over India for the examination of the equatorial and low latitude ionosphere.
The scientists observed remarkable increase of virtual height of the ionosphere to as high as 560 km over magnetic equator with vertical drift of 70 m/sec due to strong eastward direct penetration electric field which caused intense Equatorial spread F (ESF) irregularities in ionosondes and L-band scintillations in the GPS receivers across Indian region.





