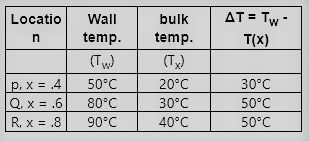
The wall of a constant diameter pipe of length 1 m is heated uniformly with flux 𝑞” by wrapping a heater coil around it. The flow at the

Q. The wall of a constant diameter pipe of length 1 m is heated uniformly with flux 𝑞” by wrapping a heater coil around it. The flow at the inlet to the pipe is hydrodynamically fully developed. The fluid is incompressible and the flow is assumed to be laminar and steady all through the pipe. The bulk temperature of the fluid is equal to 0 ºC at the inlet and 50 ºC at the exit. The wall temperatures are measured at three locations, P, Q and R, as shown in the figure. The flow thermally develops after some distance from the inlet. The following measurements are made:
| Point | P | Q | R |
| Wall Temp (ºC) | 50 | 80 | 90 |
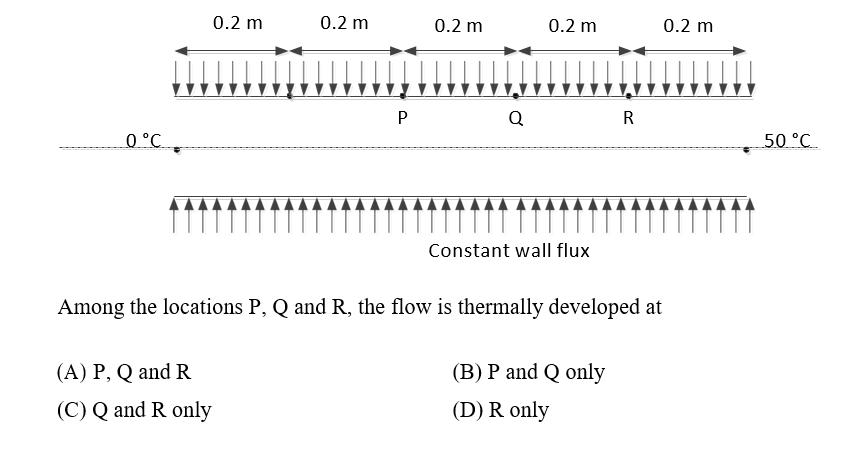
Ans: Q and R only
Sol:
Q and R only
Internal forced convection
Boundary condition: Constant Heat Flux Case
Tm(Bulk mean temperature of fluid)
At inlet, Tm.i=0∘ C
At outlet, Tm.θ=50∘ C
In case of uniform heat bulk mean temperature varies linearly. The difference between bulk mean temperature and wall temperature is constant in thermally developed region.
so bulk temperature.
T(x) = A + Bx (I)
At x = 0, T = 0°C
A = 0°C (ii)
At x = 1, T = 50°C
B = 50°C (iii)
from (i), (ii) & (iii)
bulk temperature T(x) = 50x